Wind Energy
CONSTRUCTION, MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF WIND POWER PLANTS

Harnessing the power of wind for assured sustainability
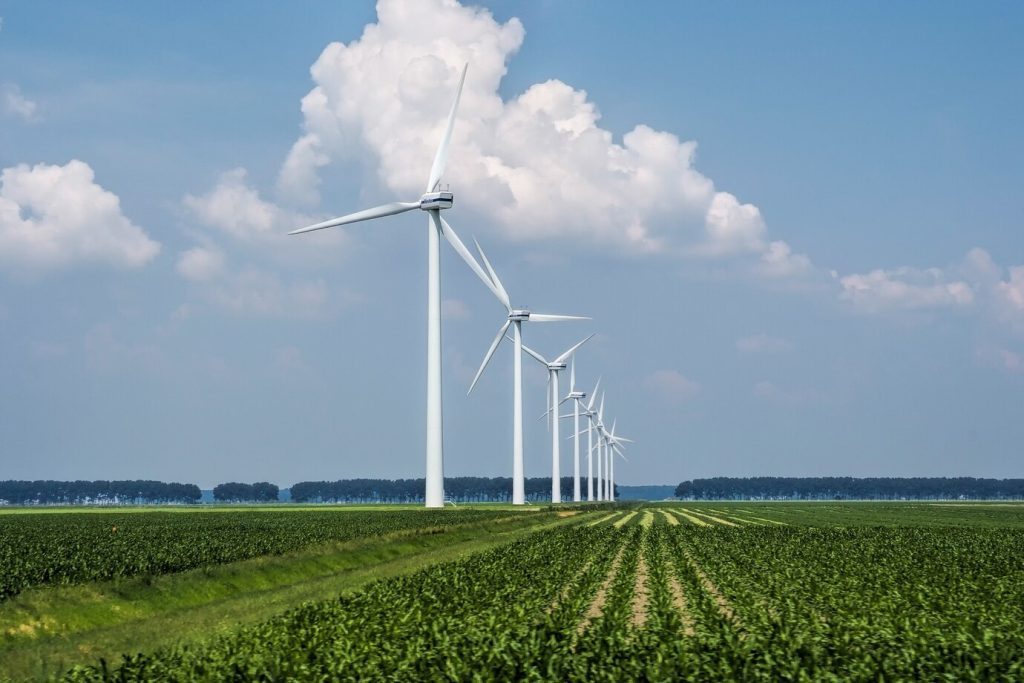
WIND ENERGY is a renewable source of great potential that transforms the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity. Through innovative wind turbine technology, this form of energy generation has become a key player in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
What is Wind Energy?
Wind energy involves the conversion of the kinetic energy of the wind into usable electricity. Wind turbines, strategically installed in areas exposed to the wind, capture the force of the wind to set the turbine blades in motion, thus generating electricity.
Wind turbines are the heart of wind energy. When the wind turns the turbine blades, a generator converts this rotary motion into electricity. Wind speed and wind turbine efficiency are crucial factors in maximising power generation.
Advantages of wind energy

Zero greenhouse gas emissions
Wind energy produces no direct emissions during operation, which contributes significantly to reducing greenhouse gases and combating climate change.

Sustainability and abundance
Wind is an inexhaustible source of energy, which makes wind energy a long-term sustainable option without depleting natural resources.

Energy self-sufficiency
By harnessing the energy provided by wind, communities can achieve a degree of energy self-sufficiency, reducing dependence on external sources.
Process of obtaining and using wind energy
Wind catchment
The process begins with the exposure of the wind turbines to the wind. Wind turbines are equipped with large blades designed to capture the kinetic energy of the wind. These blades are connected to a central shaft that rotates them when the wind hits them.
Rotation of the blades
When the wind hits the blades of wind turbines, they start to rotate. The shape and design of the blades are optimised to capture as much of the wind’s kinetic energy as possible, even at varying speeds.
Electricity generation
The rotation of the blades drives an internal generator in the core of the wind turbine. This generator converts the mechanical energy produced by the blades into electricity. The principle of operation is similar to that of a conventional generator, but instead of being driven by a motor, it is driven by the rotary motion induced by the wind.
Current transformation
The electricity generated by the generator is initially alternating current (AC). For integration into the grid or use in homes and businesses, a converter is used to transform it into alternating current, which is the standard form of electricity used in most applications.
Electricity distribution
In some cases, energy storage systems, such as batteries, are incorporated to store excess electricity generated during periods of high solar radiation. This stored energy can be used when solar production is insufficient, such as at night or on cloudy days.

Energy storage (optional)
In some cases, especially in decentralised wind energy systems, energy storage systems, such as batteries, can be incorporated to store surplus electricity generated in times of strong wind. This allows a continuous supply even when the wind speed decreases.
Monitoring and maintenance
Continuous monitoring systems enable real-time tracking of wind turbine performance. Regular maintenance ensures the long-term efficiency and durability of the WIND ENERGY system.
Types of wind power plants

Wind energy stands as a symbol of sustainability and innovation in the global energy landscape. By embracing this form of energy generation, we are not only harnessing the power of the wind to light up our lives, but also driving the march towards a future where wind energy is a predominant and clean force.
Types of energy plants include:
Onshore wind farms
Onshore facilities housing multiple wind turbines. They are common in regions with consistent winds and have different configurations depending on the topography of the site.
Offshore wind farms
Located in coastal waters, they take advantage of more constant and stronger winds. Offshore wind turbines are mounted on floating or fixed platforms on the seabed.
Small-scale wind turbines
Designed for installation in urban environments or rural communities, these individual wind turbines are ideal for localised wind power generation.
Uses of wind energy
Large-scale generation
Wind farms, both onshore and offshore, supply wind energy to the grid, powering homes, businesses and entire communities.
Wind pumps for irrigation
In remote agricultural areas, wind pumps use the energy they produce to extract water from the ground, facilitating crop irrigation.
Independent loads
Small-scale wind turbines can power stand-alone systems, such as lighthouses, communication systems or weather stations in remote locations.
Wind in favour of the future sustainable
We celebrate the renewable impulse that the wind gives us. By harnessing this natural force, we are building a cleaner and more sustainable tomorrow.
Wind energy is not just a source of electricity; it is a commitment to a future where energy is abundant, environmentally friendly and available to all.
Other energy sources



