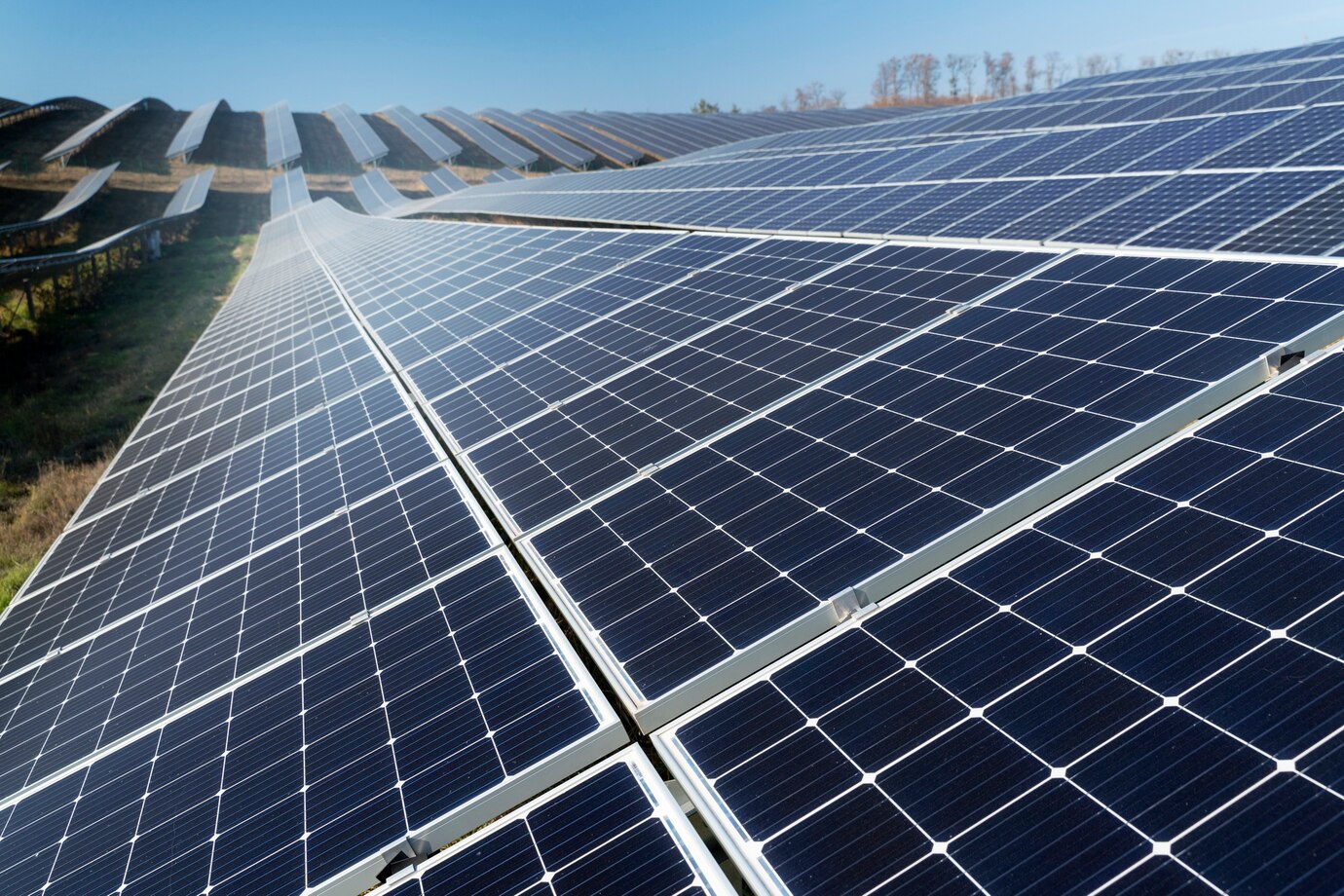
Photovoltaic Energy
CONSTRUCTION, MANAGEMENT AND MAINTENANCE OF PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER PLANTS

Capturing the Sun's Power for a Sustainable Future
PHOTOVOLTAIC ENERGY is a renewable source that uses solar radiation to generate electricity in a clean and sustainable way.
Unlike other forms of energy generation, PV does not emit greenhouse gases or deplete natural resources, making it a key option in the transition to a more sustainable energy matrix.
What is Photovoltaic Energy?
Solar energy is based on the ability of certain materials, such as silicon, to generate electric current when exposed to sunlight. Photovoltaic panels capture the energy of the sun’s photons, releasing electrons and thus creating a flow of electricity.
Obtaining photovoltaic energy begins with the installation of solar panels in areas exposed to sunlight. When photons hit the photovoltaic cells, they generate electricity directly. This process, known as the “photovoltaic effect”, is the essence of solar power generation.
Advantages of solar energy
Renewable and sustainable
Photovoltaic energy uses an inexhaustible and abundant source: sunlight, contributing to a long-term sustainable energy supply.

Zero emissions
By generating electricity without burning fossil fuels, photovoltaics produce no pollutant gas emissions, significantly reducing the carbon footprint.
Energy independence
The installation of photovoltaic systems allows households and businesses to generate their own energy, reducing dependence on external sources.

Low operating costs
After the initial investment in the installation, the operating costs for maintenance are low, which makes solar energy economically attractive.
Process of obtaining and using solar energy
Sunlight harvesting
The process begins with the exposure of the photovoltaic panels to sunlight. These panels are composed of photovoltaic cells, usually made of silicon, which have the ability to generate electricity when photons of sunlight strike them.
Direct current generation
When photons hit the photovoltaic cells, they release electrons into the semiconductor material (usually silicon). This process, known as the “photovoltaic effect”, generates a direct electric current (direct current or DC) in the photovoltaic cells.
Direct current to alternating current inversion
The direct current generated by photovoltaic panels is not directly usable for most conventional electrical applications. Therefore, an inverter is used to convert this direct current into alternating current (AC), which is the form of electricity used in homes and businesses.
Distribution and use of electricity
The electricity generated, now in the form of alternating current, is distributed via an internal electrical system or fed into the grid. In the case of grid-connected systems, the electricity can be used directly by the property where it was generated or fed into the grid for use by other consumers.
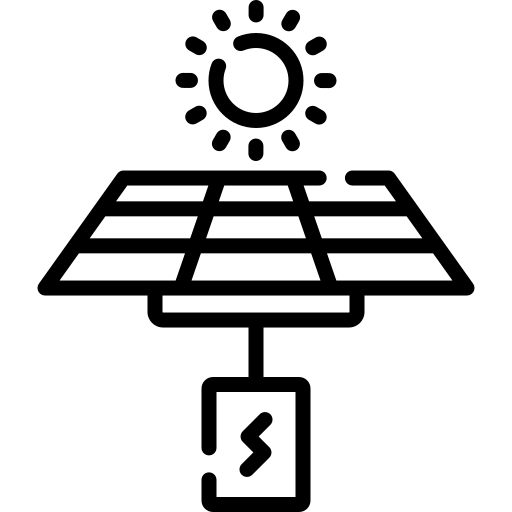
Energy storage (Optional)
In some cases, energy storage systems, such as batteries, are incorporated to store excess electricity generated during periods of high solar radiation. This stored energy can be used when solar production is insufficient, such as at night or on cloudy days.
Monitoring and maintenance
The PV system is usually equipped with monitoring systems that allow real-time tracking of electricity production. In addition, regular maintenance, which is usually minimal, ensures the efficient and long-lasting operation of the system.
Types of Photovoltaic plants

The field of solar energy is constantly evolving, driven by research and innovation. Advances in solar panel efficiency, installation techniques and energy storage ensure that this technology continues to become increasingly accessible and effective, paving the way for an even more sustainable future.
Types of photovoltaic plants include:
Roof installations
Photovoltaic panels installed on the roofs of buildings, enabling decentralised power generation for homes and businesses.
Solar farms
Large areas equipped with solar panel arrays, generating large amounts of photovoltaic energy for communities and power grids.
Floating plants
Installations on bodies of water that make use of the surface of lakes and reservoirs for photovoltaic power generation, maximising the use of space.
Uses of solar energy
Residential supply
Photovoltaic systems in homes provide CLEAN and sustainable ENERGY for daily needs, reducing dependence on the conventional electricity grid.
Large-scale generation
Photovoltaic plants supply energy on a large scale to communities, cities and even power grids, contributing to the stability and sustainability of supply.
Sustainable mobility
Photovoltaics are integrated into mobility solutions, powering electric vehicles and public transport systems.
Hybrid systems
It is combined with energy storage systems to provide energy even when the sun is not shining, ensuring a constant supply.
A respectful legacy
Solar energy represents a vanguard in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future. By embracing this technology, we are not only generating electricity, but also building a legacy of respect for our planet and generations to come. It illuminates our present and lights the way to a more sustainable tomorrow.
Other energy sources



